Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


Allisartan isoproxil + amlodipine delivers superior and sustained blood pressure control when compared to allisartan alone in essential hypertension.
According to the findings of a randomized controlled phase III trial, a fixed-dose combination of allisartan isoproxil (ALI) 240 mg and amlodipine (AML) 5 mg offers superior blood pressure (BP) control than ALI monotherapy in people with mild-to-moderate essential hypertension.
The study included 199 volunteers with mean sitting systolic BP (msSBP) between 140 and <180 mmHg and diastolic BP (msDBP) between 90 and <110 mmHg. All the subjects (age 18–70 years) initially received ALI during a 4-week run-in period before being randomized 1:1 to get either ALI/AML (n=99) or ALI alone (n=100) once daily for 12 weeks.
This phase was followed by a 40-week open-label extension, during which all patients received the ALI/AML combination, allowing long-term evaluation of effectiveness and safety. Results showed a substantially greater reduction in msSBP and msDBP at week 12 in the ALI/AML group when compared to the ALI group. Ambulatory BP monitoring further supported these findings, showing greater 24-hour systolic/diastolic BP reductions in the combination group (Table 1).
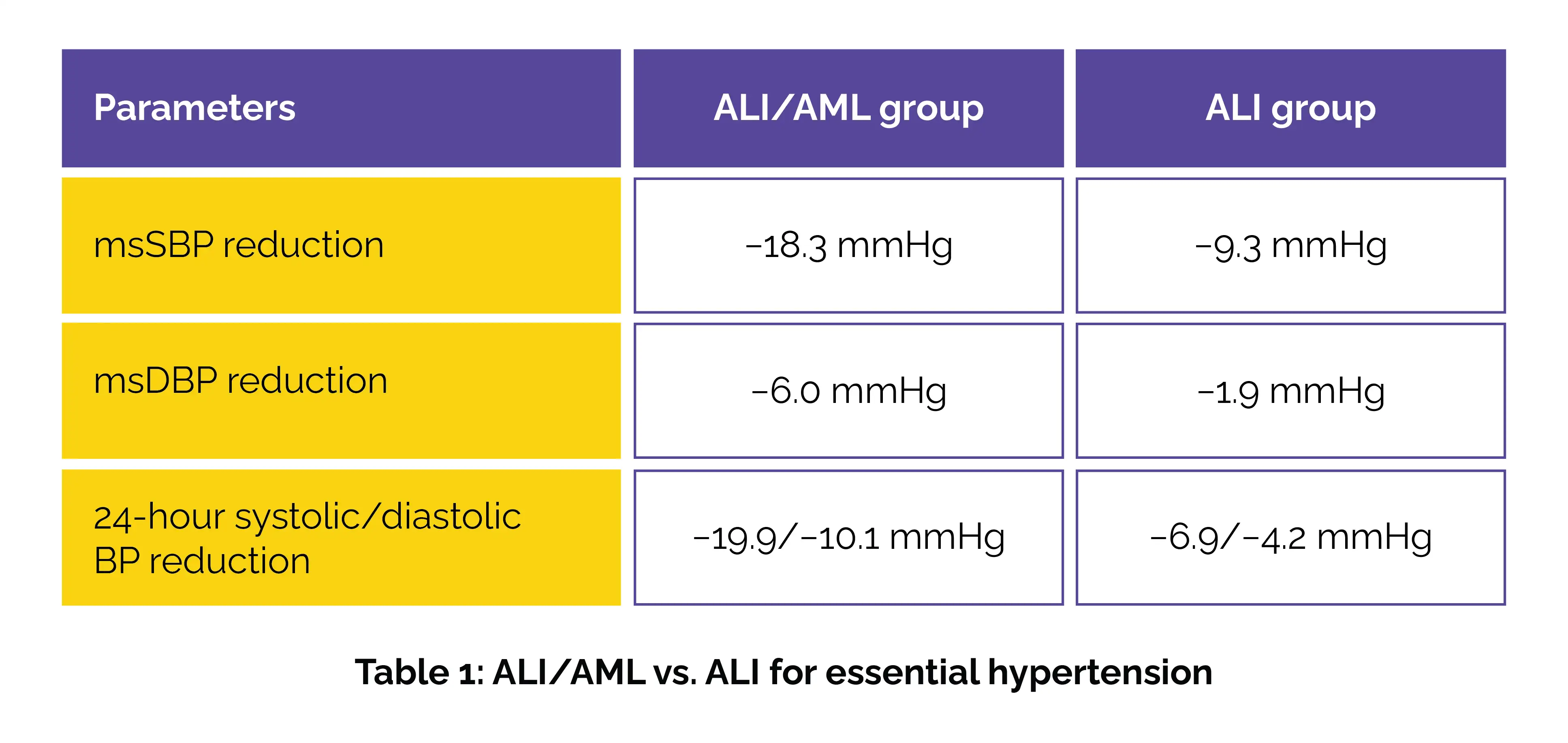
Importantly, more patients in the combination therapy group achieved target office BP (40.2% vs 20.4%) and met BP response criteria (53.6% vs 25.5%). The safety profile of the ALI/AML combination was favorable, with adverse events being mild and comparable between the groups. No novel safety concerns emerged during the 52-week period. Overall, the study demonstrates that the once-daily fixed-dose ALI/AML combination provides more effective and sustained BP control than monotherapy, with a convenient single-pill formulation that may enhance adherence and long-term outcomes in essential hypertension.
Journal of Human Hypertension
Efficacy and Safety of Allisartan Isoproxil/Amlodipine in Patients with Essential Hypertension: A Phase III, Multicenter, Double-Blind, Parallel-Group, Randomised study
Hongjie Chi et al.
Comments (0)