Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


Histaglobulin + bilastine provides faster, more effective, and well-tolerated symptom relief in patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria when compared to bilastine alone.
In a randomized clinical trial, the addition of histaglobulin to bilastine accelerated symptom relief and improved overall disease control in chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU). The study, conducted at the dermatology outpatient department of a tertiary care hospital, evaluated the effectiveness of combining histaglobulin injections with antihistamine bilastine for CSU relief. Overall, 57 adults (aged over 18) experiencing CSU symptoms for more than 6 weeks were divided into two groups:
At the outset, detailed clinical profiles were collected, including patient demographics, CSU characteristics, and baseline Urticaria Activity Scores (UAS). Additional laboratory assessments included complete blood counts, renal, liver, and thyroid function tests, serum immunoglobulin E (IgE) levels, absolute eosinophil count, vitamin B12 levels, and results from the autologous serum skin test.
UAS7 scores—a key measure of urticaria severity—were tracked weekly for 6 weeks. The primary outcome focused on changes in UAS scores, while secondary outcomes included symptom control and safety monitoring. The findings were compelling. By the 6th week, the combination group showed a higher reduction in UAS scores when compared to the monotherapy group (Table 1).
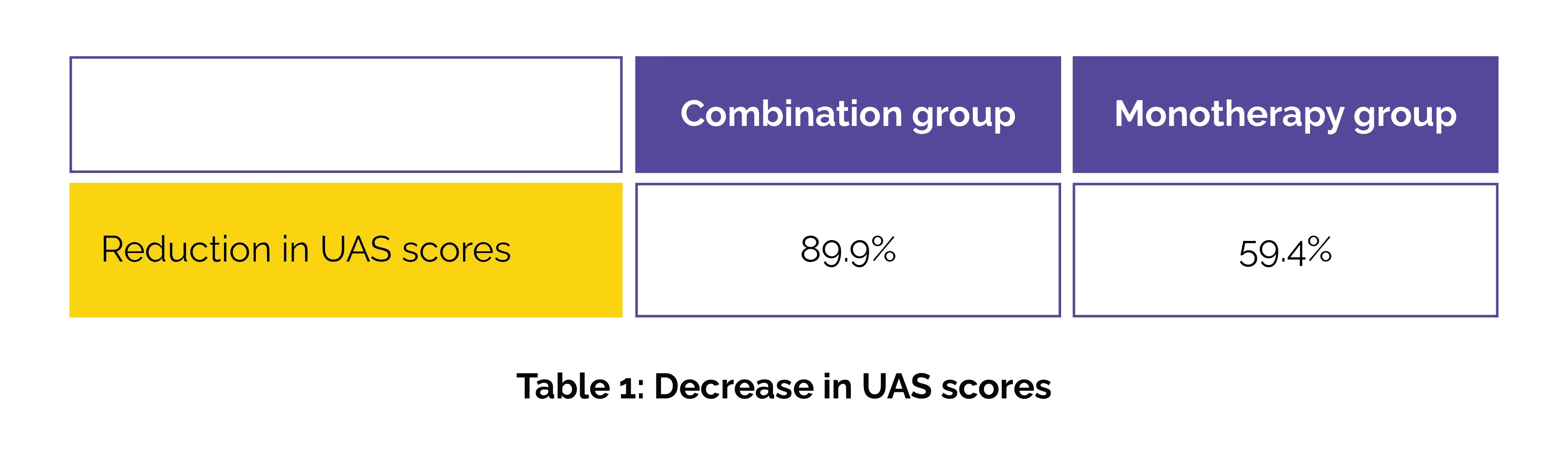
Notably, the combination group began experiencing faster symptom relief as early as week 2. Laboratory markers also improved more prominently in the combination group, with notable drops in both serum IgE and eosinophil counts—key indicators of allergic inflammation. Importantly, no adverse events were witnessed during the trial, indicating the treatment’s excellent safety profile. These results suggest that adding histaglobulin to standard antihistamine therapy can remarkably boost symptom control in CSU patients, offering faster and more effective relief.
Archives of Dermatological Research
Effect of combining histaglobulin with antihistamines in patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria in a tertiary care hospital setting- a randomized trial
Kalpana Mali Ramanna et al.
Comments (0)