Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


Many individuals with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HeFH) are unable to meet recommended low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) targets despite using multiple lipid-lowering medications.
Bempedoic acid lowers LDL-C and improves lipid parameters regardless of HeFH status, with a favorable safety profile.
Many individuals with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HeFH) are unable to meet recommended low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) targets despite using multiple lipid-lowering medications. Hence, this study sought to assess bempedoic acid's effectiveness and safety as an add-on therapy for LDL-C reduction in patients diagnosed with HeFH.
This analysis pooled data from two phase 3 clinical trials, each lasting 52 weeks, involving patients with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and/or HeFH who were receiving their maximum tolerated dose of statins. The enrolled subjects were randomly allocated in a 2:1 ratio to get either bempedoic acid or placebo, with outcomes analyzed by HeFH status. Key outcomes incorporated safety evaluations, alteration in LDL-C and other lipid measures from baseline to week 12 and up to week 52, and the proportion of patients reaching LDL-C targets.
The analysis included 217 people with HeFH (bempedoic acid: 146; placebo: 71) and 2,792 patients without HeFH (bempedoic acid: 1,864; placebo: 928). Baseline LDL-C levels averaged 172.8 mg/dL in the HeFH group and 102.6 mg/dL in those without HeFH. At week 12, bempedoic acid markedly lowered LDL-C when compared to placebo in both groups (Table 1).
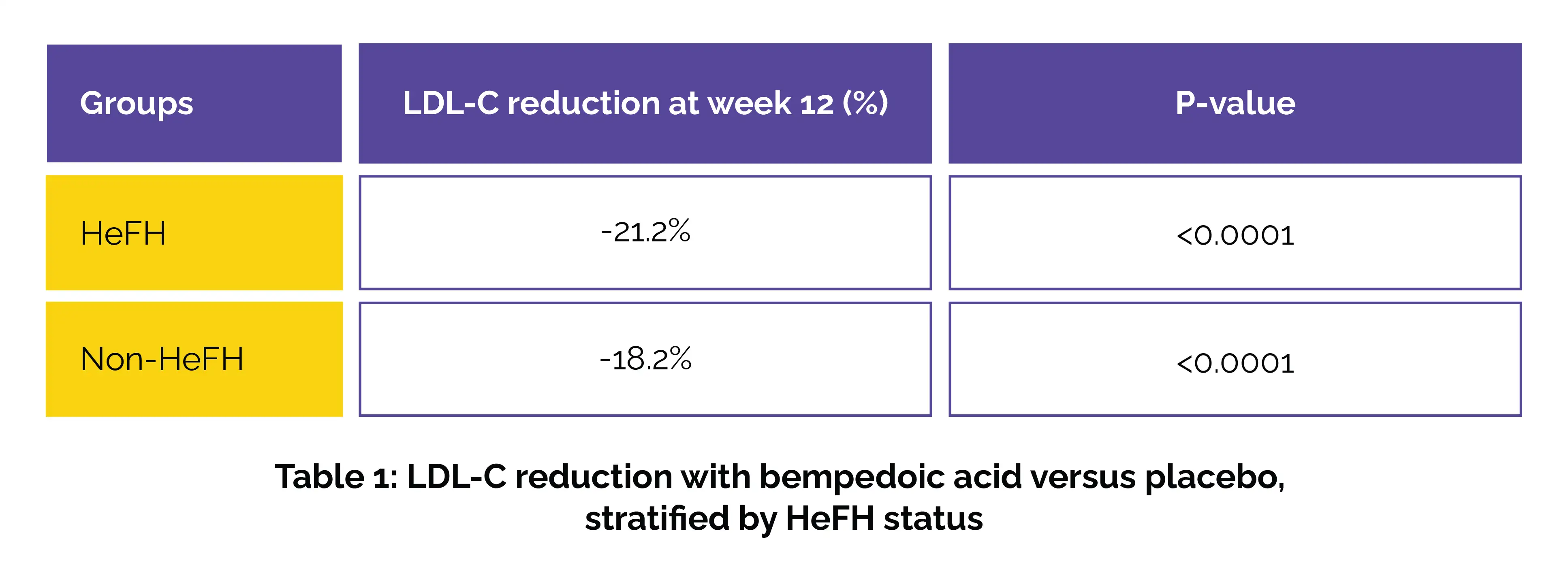
It also led to remarkable reductions in other lipid markers and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, regardless of HeFH status (all P≤0.01). In the HeFH subgroup receiving bempedoic acid, 32% reached LDL-C <100 mg/dL by week 12, and 27% by week 52. Across all groups, the rate of treatment-emergent adverse events was found to be comparable (ranging from 74.7% to 77.5%).
Bempedoic acid successfully reduced LDL-C levels and was generally well-tolerated in both HeFH and non-HeFH populations. No new safety concerns were identified in the HeFH group, even though these patients received more intensive lipid-lowering therapy.
Journal of Clinical Lipidology
Efficacy and safety of bempedoic acid in patients with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia: analysis of pooled patient-level data from phase 3 clinical trials
P Barton Duell et al.
Comments (0)